Climate change is a challenge for the global lake ecosystem. Phytoplankton is an important primary producer in the lake ecosystem, and is strongly influenced by the changes of the environment, so it is an ideal organism to study the impacts of climate change on the lake ecosystem. By analyzing the temperature and radiation of the past 60 years in eastern China, the ecosystem dynamics research group from Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology Chinese Academy of Sciences found that in our eastern country during the late 1980s temperature rose significantly and scattered radiation increase is an important factor to the temperature rise (Picture 1, International Journal of Climatology, 2015). There is an interactive effect of nutrients and water temperature. Phytoplankton community composition was mediated by nutrients concentrations, but this effect was strongly enhanced by elevated water temperatures (Picture 2). 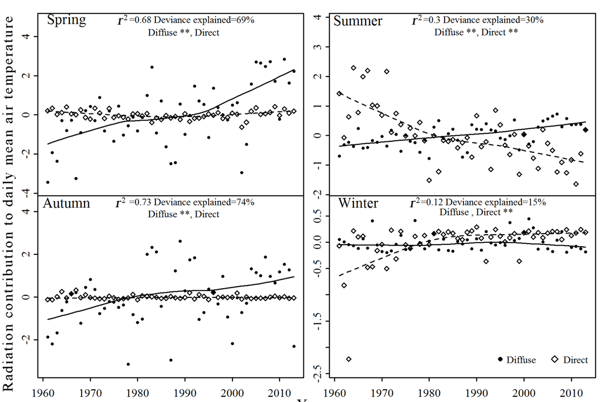
Picture 1 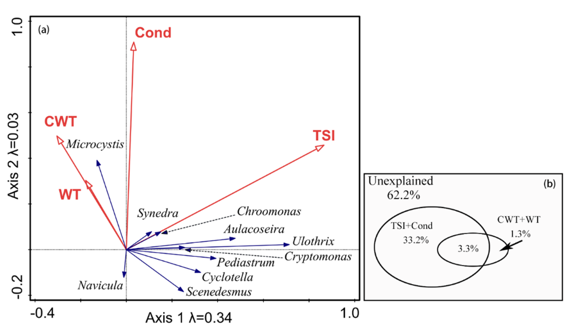
Picture 2 JM Deng, YL Zhang, BQ Qin, K Shi. Long-term changes in surface solar radiation and their effects on air temperature in the Yangtze River Delta. International Journal of Climatology 2015, 35(12): 3385-3396. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0088 JM Deng , BQ Qin et al. Earlier and warmer springs benefit cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in subtropical Lake Taihu, China. Freshwater Biology 2014, 59: 1076-1085. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/fwb.12330/abstract JM Deng , BQ Qin et al. Effects of nutrients, temperature and their interactions on spring phytoplankton community succession in Lake Taihu, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9(12): e113960. http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0113960 (Information source: Nanjing branch of CAS) |

