Recently, the group led by Wei Chen from Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has successfully prepared graphene stabilized silver nanoparticles electrochemical electrode, which establishes the foundation of designing novel Ag-based ionic polymer nano-composite actuator device. This work has been recently published in Advanced Materials online, 2012, DOI: 10.1002/adma.201203655.
Ionic polymer metal composite is a new type of smart materials, which can be widely used in bionic robot, micro medical devices, microfluidic, human-computer interaction, and other fields. Their typical bimorph structure is composed of one ionically conductive electrolyte membrane laminated by two electrically conductive electrode membranes, which can bend to allow the redistribution of different-size cations and anions under applied voltage. Their actuation performance is largely influenced by the properties of the electrode materials. The exploitation of electrodes with high conductivity and electrochemical stability are thus highly desirable.
It has long been known that metals can act as good conducting media. However, they all face terrible corrosion problem. Surface coating is an effective technology for anti-corrosion. The mechanism lies in preventing the surface from contacting with corrosive media.
Inspired by this technique, Prof. Chen’s group developed a way to use graphene for anti-electrochemical corrosion of silver nanoparticles. Graphene, the quasi-two dimensional carbon nanomaterials, has been proved to be a stable electrochemical electrode material. Silver owns superior electrical conductivity as well as easy corrosion. The typical wrapping of graphene on silver surface inhibited the interfacial electrochemical redox reaction.
As a result, hybrid material preserved its high electrical conductivity and good electrochemical stability. Bimorph ionic actuator constructed from the hybrid electrode has shown largely improved electrochemical and mechanical performance along with highly cyclic stability. This work further develops the electroactive polymer artificial muscle materials.
They believe the strategy of hybridizing RGO and AgNPs could be of great value for further developing more RGO/metal hybrid–based electrochemical actuators or sensors for various applications. This work is supported by national natural science foundation, Ministry of Science and Technology and natural science foundation of Jiangsu.
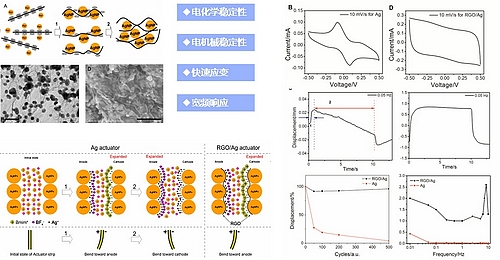
Schematic diagram of electrode fabrication, SEM images, schematic diagram of electrochemical and electromechanical process.
(Information source: Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics of CAS)

